우선순위 큐란?
우선순위를 가진 데이터들을 저장하는 큐를 의미한다.
데이터를 꺼낼 때 우선 순위가 높은 데이터가 가장 먼저 나온다는 특징이 있다.
운영체제의 작업 스케줄링, 정렬, 네트워크 관리 등의 다양한 기술에 적용되고 있다.
우선순위 큐와 큐의 차이점
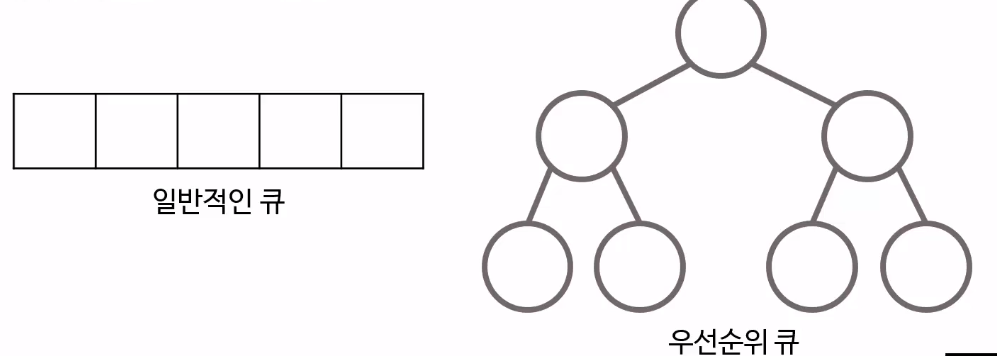
일반적인 큐는 선형 구조를 가지고 있지만 우선순위 큐는 트리(Tree) 구조로 보는 것이 합리적이다.
일반적으로 우선순위 큐는 최대 힙을 이용하여 구현한다.
최대 힙(Max Heap)
최대 힙은 부모 노드가 자식 노드보다 값이 큰 완전 이진 트리이다.
우선순위 큐의 삽입
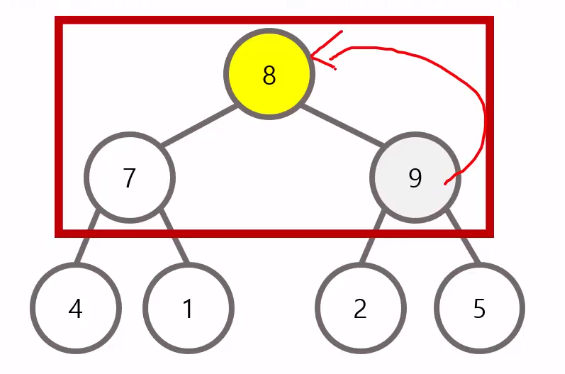
완전 이진 트리를 유지하는 형태로 순차적으로 삽입된다.
삽입 이후에는 루트 노드까지 거슬러 올라가면서 최대 힙을 구성한다.(상향식)
우선순위 큐의 삭제
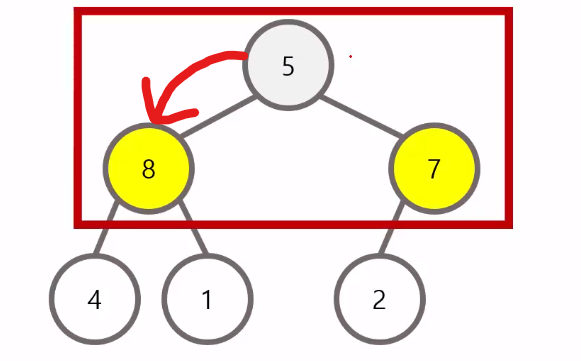
삭제할 때는 루트 노드를 삭제하고, 가장 마지막 원소를 루트 노드의 위치로 옮긴다.
삭제 이후에는 리프 노드까지 내려가면서 최대 힙을 구성한다.(하양식)
코드
// 우선순위 큐
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10000
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
typedef struct {
int heap[MAX_SIZE];
int count;
} priorityQueue;
void push(priorityQueue *pq, int data) {
if (pq->count >= MAX_SIZE) return;
pq->heap[pq->count] = data;
int now = pq->count;
int parent = (pq->count - 1) / 2;
// 새 원소를 삽입한 이후에 상향식으로 최대 힙을 구성한다.
while (now > 0 && pq->heap[now] > pq->heap[parent]) {
swap(&pq->heap[now], &pq->heap[parent]);
now = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
pq->count++;
}
int pop(priorityQueue *pq) {
if (pq->count <= 0) return -9999;
int result = pq->heap[0];
pq->count--;
pq->heap[0] = pq->heap[pq->count];
int now = 0, leftChild = 1, rightChild = 2;
int target = now;
// 새 원소를 추출한 후에 하향식으로 힙을 구성한다.
while (leftChild < pq->count) {
if (pq->heap[target] < pq->heap[leftChild]) target = leftChild;
if (pq->heap[target] < pq->heap[rightChild] && rightChild < pq->count) target = rightChild;
if (target == now) break; // 더 이상 내려가지 않아도 될 때 졸료
else {
swap(&pq->heap[now], &pq->heap[target]);
now = target;
leftChild = now * 2 + 1;
rightChild = now * 2 + 2;
}
}
return result;
}
int main(void) {
int n, data;
scanf("%d", &n);
priorityQueue pq;
pq.count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &data);
push(&pq, data);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int data = pop(&pq);
printf("%d ", data);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}'C자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자료구조: 그래프의 개념과 구현 (0) | 2019.09.05 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조: 순차 탐색(Sequential Search) & 이진 탐색(Binary Search) (0) | 2019.08.30 |
| 자료구조: 이진 트리(Binary Tree) (0) | 2019.08.29 |
| 자료구조: 기수 정렬(Radix Sort) (0) | 2019.08.29 |



댓글